Business Modeling
Business Component
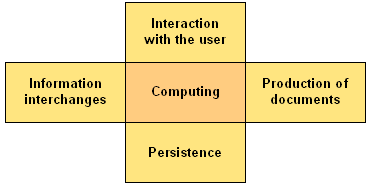
It can be associated a micro and dedicated information system called business component to each activity done by an actor of the firm. We find in it the essential functions that are following:
- Interaction with the user.
- Information interchanges.
- Production of documents.
- Persistence.
- Computing.
The component beholds the modeling of the atomic activity for what can be automated. This abstraction is described at the IT level by the business interface, which is independent of:
- Any kind of use.
For example, a human-machine interface, a batch program loading a data stream, a report, etc.
- Any kind of setting-up.
For example, by integrating a function of specific vertical software or a dedicated development, etc.
- Any technologies.
For example in client-server, in thin client; recording into a Db2 database on Z/Os or Oracle on Linux, etc.
Business Interface
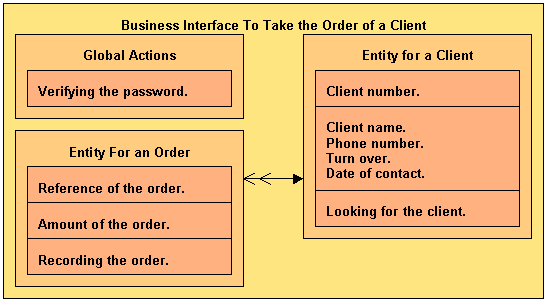
The business interface describes in an exhaustive way the part of the activity to automate:
- Information.
It is gathered into entities such as a client, an order or an invoice. A business interface beholds some properties:
- A unique identification key.
This is for example the client number, the order or invoice reference.
- Properties perhaps.
For a client, this is for example his name, his phone number, the turnover realized with him, the date to which he got in touch with the firm the first time. A property is thus characterized by:
- Its type.
The most usual types are the character string - for the name -, the integer - for the phone number -, the real - for the turnover - and the date - for the contact date.
- Its size.
For example, le the name of the client can have up to 30 characters.
- Its compulsory status.
For example, the client has obviously a name but not compulsorily a phone number.
- The relations between entities.
A relation is a link between two entities such as the orders realized by a client. A relation beholds:
- A sense.
- A cardinality.
- Properties perhaps.
- The actions.
They can be:
- Independents of entities.
For example, the action of "verifying a password" while starting up the application.
- Peculiar to one of them.
For a client, an action can be "to find the client" ; for an order, an action can be "to record the order" ; for an invoice, an action can be "to print the invoice", etc. We are talking then about methods.
Business Modeling
While the function conception stage of an application, the business interfaces of atomic activities that are entering into the perimeter are defined. From time to time, while running the processes, it is possible to build the business modeling of the enterprise of the public service, through the clustering and the completude of different business interfaces.
The interconnections of applications, what are translated in the day-to-day work into information system as data flows and service calls, are characterized by shared business interfaces.
Here is an example:
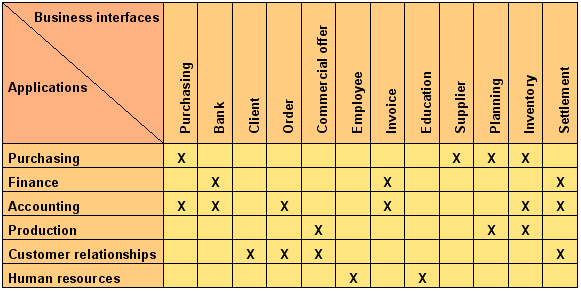
A shared business interface may be too rich for an application. In this case, in order to simplify the local modeling, it is possible to use a business view by only keeping information, the relations and the actions that are just necessary.
Building an information system around a business modeling designed with business interfaces is offering two major benefits for the firm:
- Two applications that are setting up a business interface can be exchanged without any incidence for the other applications that the one that is not interconnected to.
The cost of projects is lower by this way.
- The flow of information is ease.
Since the logical formats of information are the same due to the shared business interfaces.
Business Expertise Rules
The business modeling conceptualizes information kept and exchanged inside the firm and also the actions that are impacting their life cycle - creating, modifying, reading, transferring and deleting.
The business modeling is however not concerned by the state of art and the know how of the firm, coming from year experience feed by numerous competencies, that have contributed to its positioning and its culture.
The purpose of the business expertise rules is to fill this lack by making explicit this expertise, which is mostly proper to the firm. They act as triggers on the business modeling.
Here is an example that could apply to a business interface describing a client in the telecom business line:
If the invoice of the client is lower that one Euro then do not claim for payment.
The reason is not to have bank fees upper than the turnover.
If the consumption of the client is 25% upper than his average consumption, then ask for an advance on consumption.
The reason is to manage the non-payment risk.
If the client risk is strong, then settle his account from the Société Générale's one.
The reason is that non-payment fees are lower in Société Générale in regard with other banks.
If the client is using the "Souplessismo" offer, then register him into the statistics.
The reason is that the offer "Souplessimo" is in the launching stage. We must keep an eye on the conquest curve.
|



